R&D
Amber Research and Development



























Amber Biotechnology
The history of amber research and its results will be unraveled.

Keiji Kondo
Part-time Director, Amber Biotechnology, Inc.
Few in the world have been able to scientifically demonstrate what amber does and how it works."
Amber Biotechnology began its history of amber research as a challenge to the totally "unknown" and has now acquired a vast amount of research results and knowledge about amber. Our first efforts in basic amber research were the development of succinic powder. We developed a new amber pulverization technique to make the powder even finer than the powder used for amber therapy in Russia. We succeeded in creating a finer, smoother powder that could be used in cosmetics. In 2005, this powder was granted patents (Patent No. 3725848 and No. 3741429) as KOHAKU POWDER® (PD) for "prevention of fading of natural pigments in cosmetics. In addition, the start of joint research on amber with the (now) National Institute of Physical and Chemical Research (RIKEN) greatly accelerated our research on the extraction and purification of active ingredients.
We went through a lot of trial and error to figure out what to soak, at what temperature, for how long, and what ingredients to extract."
The "skin turnover promotion effect (2008)" and "hyaluronic acid production promotion effect (2009)," which contribute to the creation of beautiful skin, were first discovered through the painstaking extraction of extracts using fine amber powder particles and after a tremendous number of failures and modifications. For these effects, we obtained a patent in 2012 as Kohaku Extract® Repair (RE) (Patent No. 4953204, Patent No. 4953203). We also discovered "hair growth effect (2010)" and "whitening effect (2011)" from another extraction method, and succeeded in obtaining patents in 2015 as Kohaku Extract® Grow (GR) and Kohaku Extract® White (WH), respectively (Patent No. 5858561, Patent No. 5858562).

It is attracting attention as a material with the potential for new physiological activity.
Amber Biotechnology established a central laboratory within the University of Tsukuba in 2017 as a University of Tsukuba venture to continue exploring the unknown possibilities of amber, including its health and beauty benefits. Many useful physiological activities have been reported for substances contained in plants. Amber contains unknown components produced in the process of fossilization of plant resins, and is expected to be a material with various possibilities. We have published a number of papers and publications on our research findings on amber, and in 2013, one of our papers published in the Journal of the Japanese Society of Aesthetic Dermatology won the Best Paper Award. The relentless research conducted by industry and academia, and the passion of the researchers who support them, are gradually but surely leading to the unraveling of the mysteries of amber.
Researchers have unraveled
Amber extract for food for health and
Effects of Amber Extract for Beauty
Amber extract for food
-
Chapter.1
Lipolysis promotion effect
Inhibition of fat accumulation01Looks don't do it justice.
Increase in "visceral fatVisceral fat is the storage of energy we need to carry out our daily activities. Therefore, if we do not use energy or take in excessive amounts of energy, the amount of fat will increase.
As visceral fat increases, neutral fat in the blood also increases, and HDL (good) cholesterol tends to decrease while LDL (bad) cholesterol tends to increase. Visceral fat is mainly found around the intestines. Visceral fat tends to accumulate mainly around the intestines, but since it is not visible from the outside, it is important to prevent it in daily life.
02Lipolysis Mechanism and Function of Amber Extract for Food
Lipolysis MechanismAmber extracts for food use are
when it works
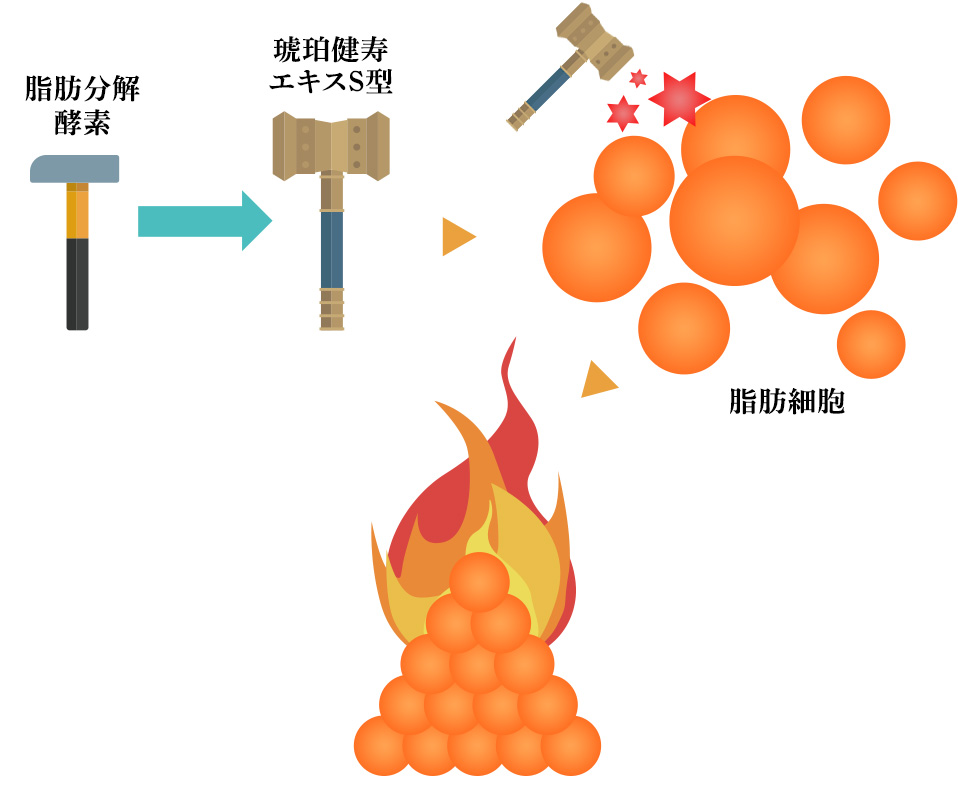
Fat in the body is broken down by lipolytic enzymes. The pieces of fat that are broken down are burned and act as energy.
03in cellular experiments.
Inhibitory effect of amber extract for food on fat accumulationtest
methodMature adipocytes (differentiated 3T3-L1 cells) from mice were fed with food-grade amber extract and cultured for 96 hours
(A) Cell viability of amber extract for food use by MTT method.
 result
resultUp to 50 µg/mL of food-grade amber extract dry solids was found to have no effect on cell viability
(B) After fixation with paraformaldehyde, fat droplets in the cells are stained red using Oil Red O
 result
resultThe more amber extract for food was given, the more the reddish area = fewer fat droplets were found
(C) Cells stained with (B) are lysed with isopropanol,
Triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in fat droplets measured at 490 nm result
resultTriacylglycerol in fat droplets decreased as the amount of food amber extract given increased
When mature cultured adipocytes were cultured with food-grade amber extract, it was found that the amount of neutral fat stored in the adipocytes was reduced compared to those that were not cultured with the extract.
Excerpted from Sogo et al. Molecules Vol. 26, 4630, 2021
-
Chapter.2
Effect on glucose metabolism
By amber extract for food
Suppresses the absorption of sugar01What are the harmful effects of excessive sugar intake?
We consume carbohydrates through our diet. When carbohydrates are digested in the body, they are broken down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. The concentration of glucose in the blood is called "blood glucose level. Normally, the human body regulates blood glucose levels through the secretion of hormones. However, if a person's diet is unbalanced, with excessive intake of carbohydrates, alcohol, and sweets, the secretion of hormones cannot keep up, and a state called "hyperglycemia" occurs. The disease that results from chronic high blood sugar is diabetes, which can lead to a variety of other adverse effects on the body.
02Sugar absorption mechanism and
Function of Amber Extract for FoodSugar absorption mechanismof amber extract for food use.
Absorption mechanism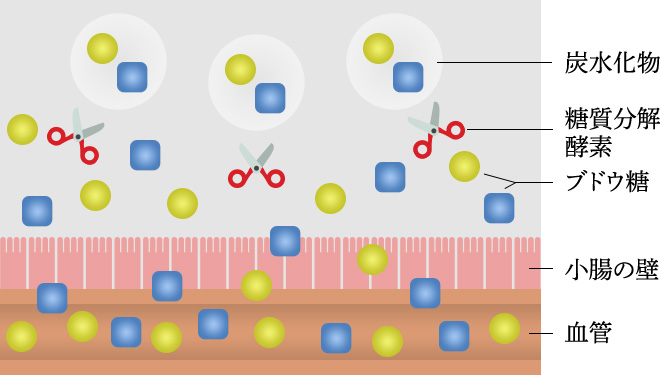
Food-grade amber extract has the effect of preventing the production of more carbohydrate-degrading enzymes than necessary for the breakdown of carbohydrates into glucose (Block 1). This two-step inhibition results in a reduction in the amount of glucose that enters the bloodstream and is absorbed into the body. The unabsorbed glucose is then excreted out of the body.
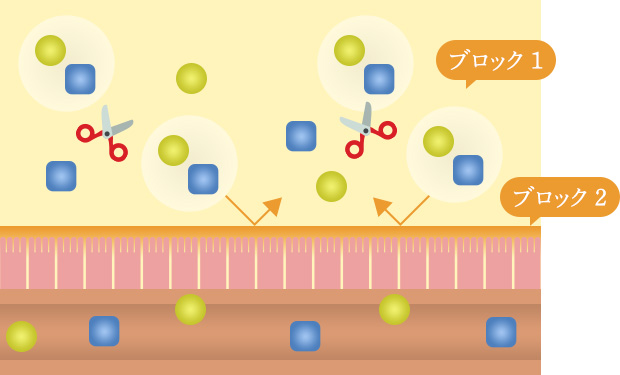
Food-grade amber extract has the effect of preventing the production of more carbohydrate-degrading enzymes than necessary for the breakdown of carbohydrates into glucose (Block 1). This two-step inhibition results in a reduction in the amount of glucose that enters the bloodstream and is absorbed into the body. The unabsorbed glucose is then excreted out of the body.
03Amber Extract for Food in Cell Experiments
double-blocking effectAInhibition of sugar degradation
test
methodHuman colon cancer-derived cells (Caco-2 cells are given food-grade amber extract and cultured for 8 days
⇒Dissolves cells and is a carbohydrate-degrading enzyme
Proteins of the sucrase-isomaltase complex (hereafter referred to as SI proteins) were detected by Western blotting. Similarly, β-actin protein was detected as an internal standard.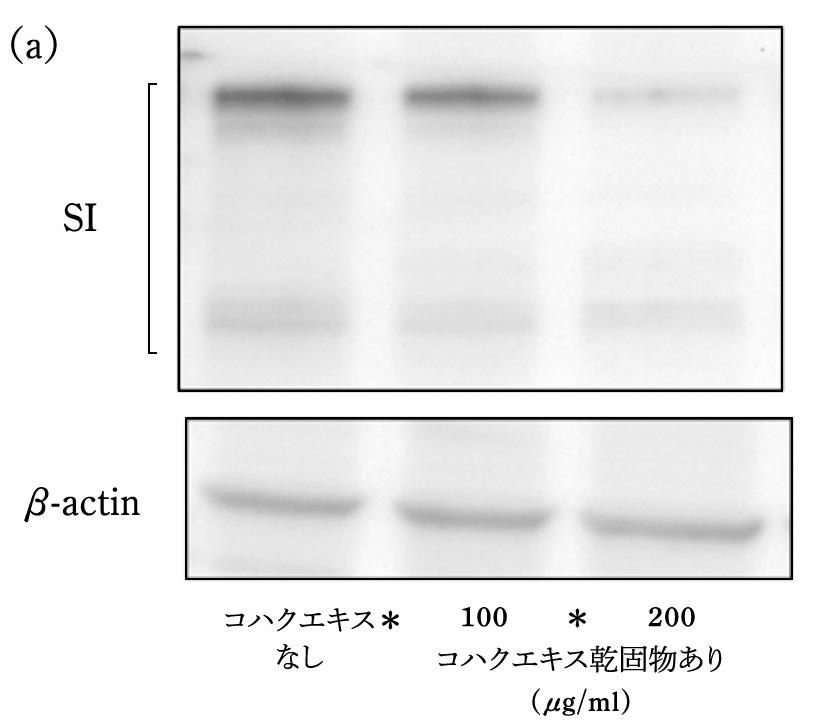
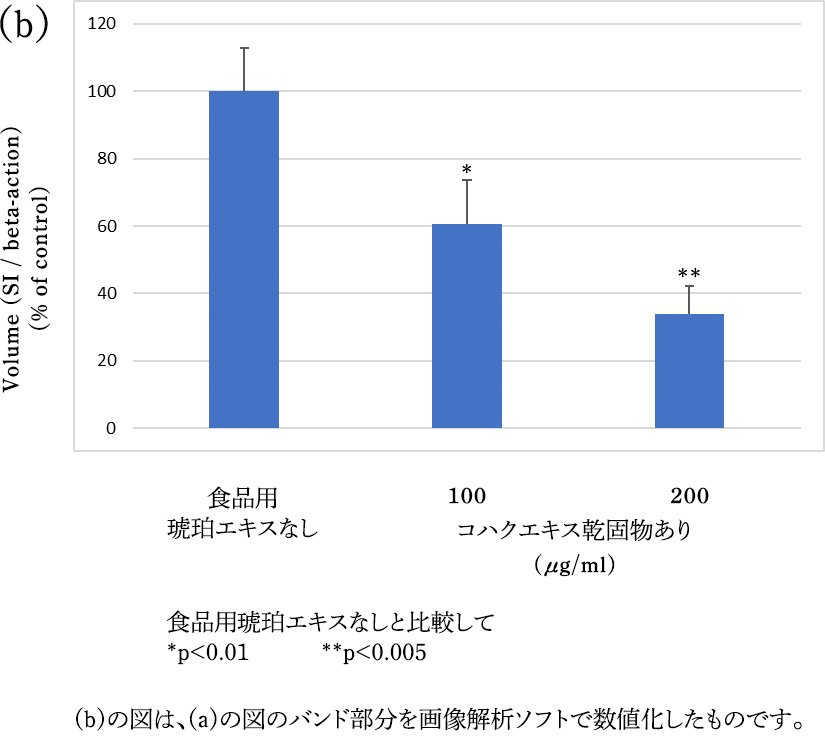 result
resultCarbohydrates ingested as food are converted to glucose from SI proteins in the small intestine and absorbed into the blood. The expression of SI protein was suppressed in those fed food amber extract compared to those not fed food amber extract. From this result, it was expected that food amber extract has an effect to suppress the absorption of sugar by suppressing the activity of carbohydrate-degrading enzymes.Excerpt from Patent No. 6599592
BInhibition of sugar absorption
test
methodCultured human colon cancer-derived cells (Caco-2 cells) on Transwell membrane filters for 3 weeks.(*Normally, 0.4-μm pore size membrane filters allow glucose to pass through)
Intercellular electrical resistance is confirmed to be 350 Ω-cm2 or higher. *
Glucose and food amber extract were added to the upper layer and incubated for 2 hours. The amount of glucose transferred to the lower layer was then measured.
Reconfirmation that intercellular electrical resistance is greater than 350 Ω-cm2.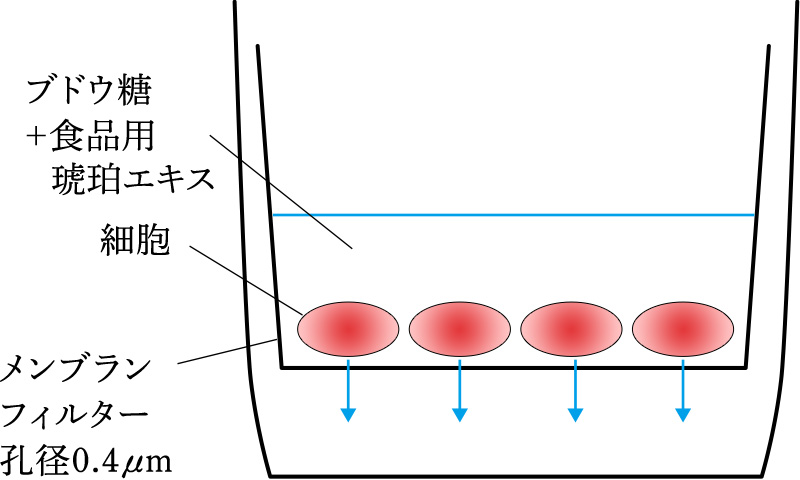
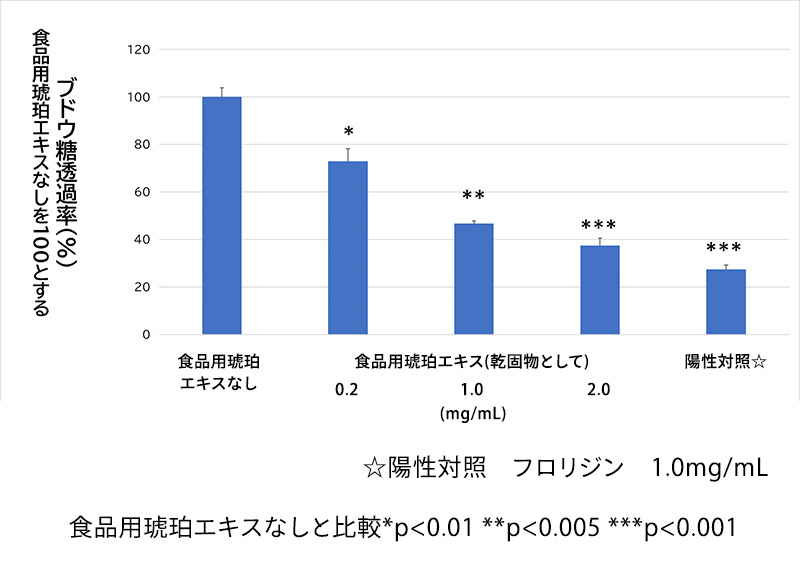 result
resultIt has been found that there are membrane proteins in the intestinal tract that selectively permeate glucose. It was found that cells with more food-grade amber extract were less permeable to glucose.Drawing based on the example of patent No. 6601860*The intercellular electrical resistance value is a guide to confirm whether or not Caco-2 cells are tightly bound together. 50 Ω-cm2 or higher is considered to indicate that they are tightly bound together and form a barrier.
-
Chapter.3
Effect on blood pressure regulation
By amber extract for food
Normal blood pressure" effect01Common among the Japanese.
Mechanism of "hypertensionBlood pressure is controlled by the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves). The autonomic nervous system (sympathetic nerves), which responds to "emergency reactions" to protect oneself from external enemies, puts the body in a state that is suitable for movements such as fighting or fleeing, and the same reaction occurs when the body experiences strong stress.
The greater the mental and physical stress, the more active the autonomic (sympathetic) nervous system becomes, resulting in an increase in heart rate. This means that the heart has to pump more blood, resulting in "high blood pressure. In addition, excessive salt intake and excessive alcohol consumption can also cause blood pressure to rise.
02The mechanism of elevated blood pressure and
Function of Amber Extract for FoodMechanism of blood pressure elevationof amber extract for food use.
mechanism of action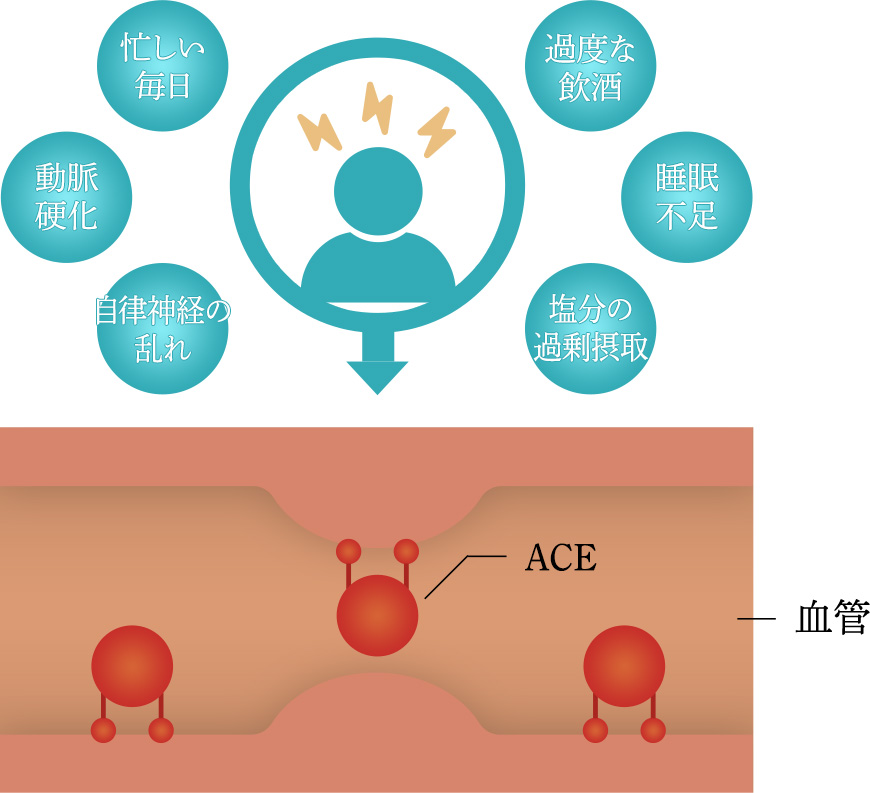
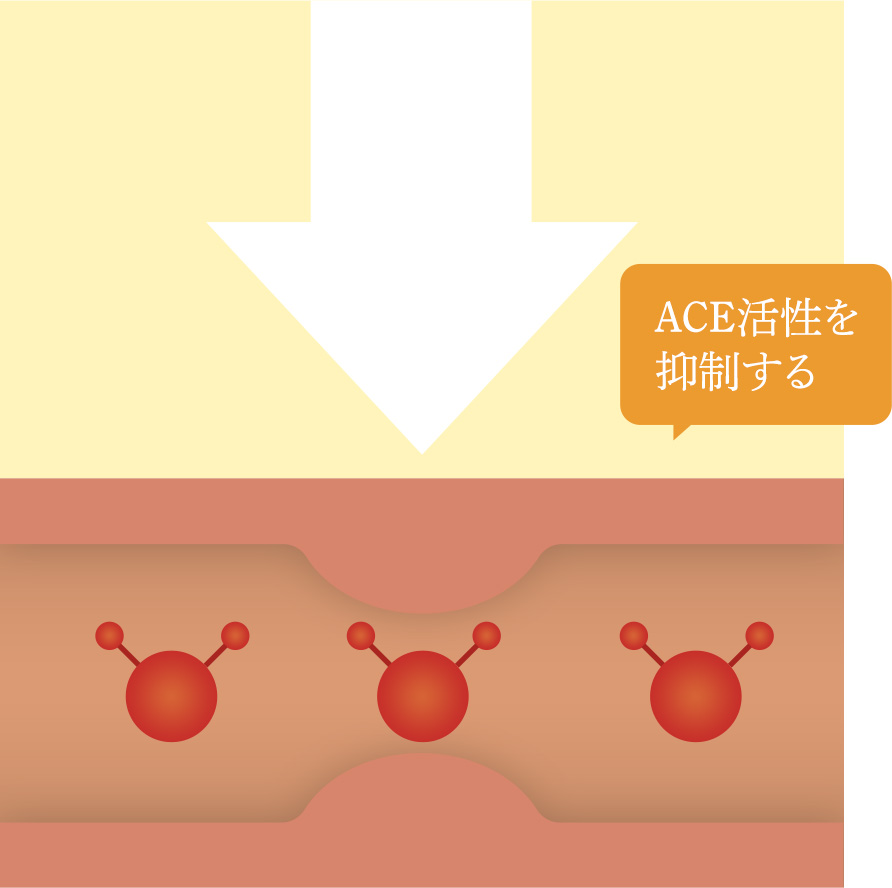
When exposed to mental or physical stress, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) is activated and blood pressure rises*1 in an attempt to shrink blood vessels. Amber extract for food can act on this ACE and inhibit its activation, thereby reducing the increase in blood pressure.
1 In fact, substances generated by ACE activation constrict blood vessels.
03Amber Extract for Food in Cell Experiments
Inhibition of blood pressure elevationtest
methodMeasured using the Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Activity Assay Kit (Dojin Chemical Co., Ltd.). 10 mg of amber extract for food (dry solid) was dissolved in 1 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, and the supernatant after centrifugation was used as the stock solution. This solution was diluted 5-fold with pure water. To these samples, substrates and enzymes were added and reacted, and the substances produced were quantified.
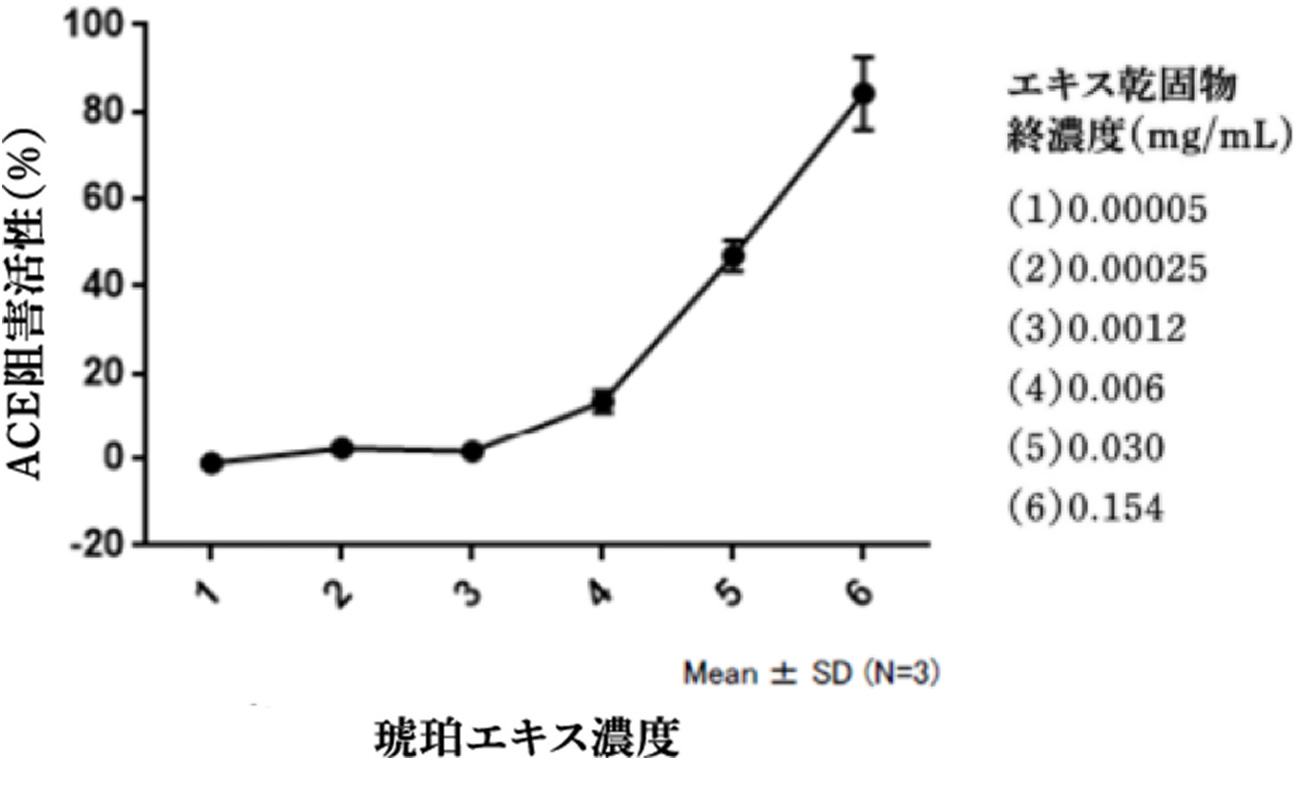 Conclusion.
Conclusion.It was found that the rate of inhibition of the enzyme ACE (angiotensin converting enzyme) activity increased as the concentration of the food amber extract increased. It was thought that food amber extract has the potential to be applied to foods and other products that suppress elevated blood pressure.Excerpt from an example from Patent No. 6548797
Amber extract
-
Chapter.1
by Kohaku Extract® Repair (RE)
Aging care of epidermis and stratum corneumSkin turnover promotion effect (Patent No. 4953204)Kohaku Extract® Repair (RE) is
Leads to normal skin renewal,
By smoothing out rough skin,
It produces a beautiful skin effect.Amount of genes that promote turnover
test
methodAfter 24 hours of culture of normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) with Kohaku Extract Repair (RE), total RNA was collected and the amount of gene (HB-EGF)*) that promotes turnover was measured by RT reaction → real-time PCR method.What is HB-EGF?
Heparin-Binding EGF-like Growth Factor stands for heparin-binding epidermal growth factor. It is a growth factor involved in skin wound healing.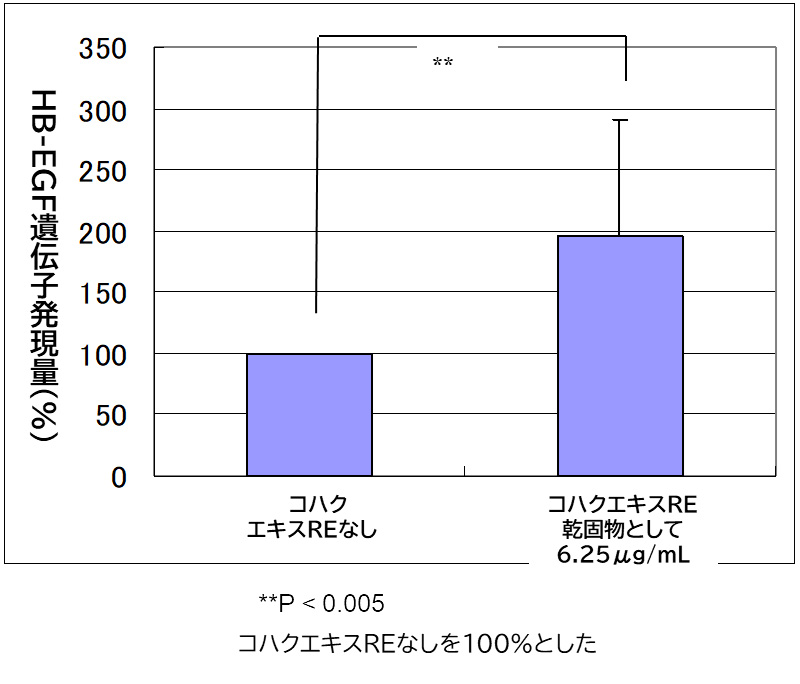 result
resultFor smooth skin
Promotes skin renewalCompared to cells without Kohaku Extract Repair (RE), the amount of HB-EGF gene was increased in cells given Kohaku Extract Repair (RE). This indicates that Kohaku Extract is expected to be effective in normalizing the turnover rate, which tends to be delayed due to aging.Excerpted from Ohara et al. Journal of Cosmetic Chemistry 34. 89-101, 2010
Hyaluronic acid production promoting effect (Patent No. 4953203)Kohaku Extract® Repair (RE) is
Increased skin moisture content,
It leads to fresh and plump skin.Amount of hyaluronic acid producing enzyme gene
test
methodHuman immortalized epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) were cultured with Kohaku Extract Repair (RE) cells for 24 hours, and total RNA was collected and the amount of hyaluronic acid producing enzyme 3 (HAS3) gene was determined by RT reaction → real-time PCR method.
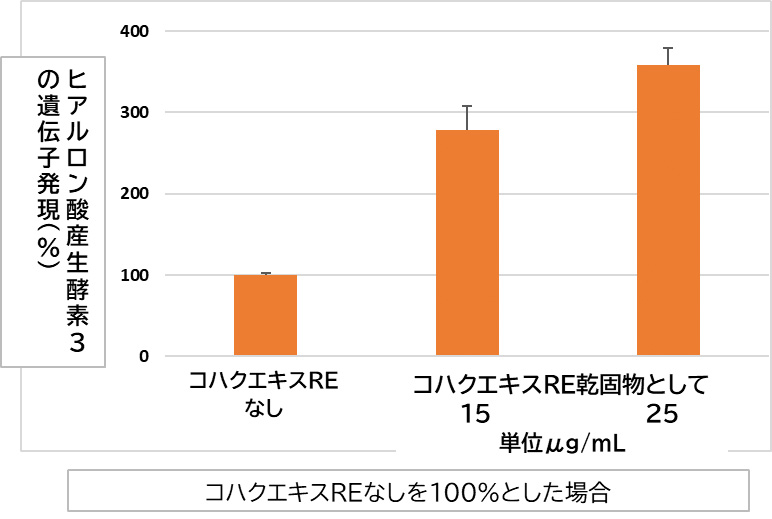 result
resultFor fresh skin
Increased skin moistureCompared to cells without Kohaku Extract Repair (RE), cells treated with Kohaku Extract Repair (RE) had increased levels of hyaluronic acid-producing enzyme 3 genes, which are involved in the production of hyaluronic acid by epidermal keratinocytes. This indicates that Kohaku Extract is expected to enhance the skin's ability to produce hyaluronic acid and retain its own moisture.Based on Ohara et al.
Stained image of hyaluronic acid
test
methodHuman skin reconstruction culture model*) (hereafter referred to as "skin model") was incubated with succinic extract repair (RE) at a final concentration of 25 μg/mL for 40 hours. The tissues were then fixed using paraformaldehyde and glutaraldehyde, and hyaluronic acid was stained brown.*Human skin reconstruction model
The skin consists of three layers from the top: stratum corneum, epidermis, and dermis, and this structure is reproduced by cultured cells. The function of human skin tissue is reproduced, albeit to a limited extent.Stained image of hyaluronic acid
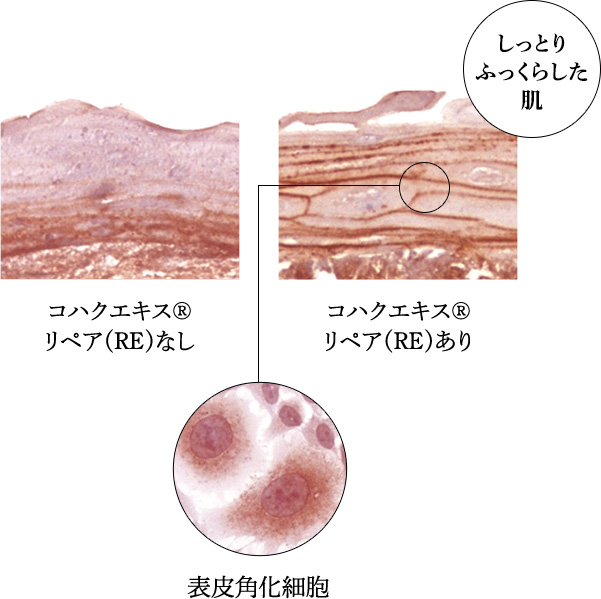 result
resultCompared to the skin model without Kohaku Extract Repair (RE), the skin model treated with Kohaku Extract Repair (RE) showed a darker brown color, especially in the epidermis, indicating that more hyaluronic acid was produced.Based on Ohara et al.
-
Chapter.2
Kohaku Extract® Grow (GR)
hair growth spurtEffect of increasing VEGF gene (Patent No. 5858561)With KOHAKU EXTRAX® GROW(GR)
By processing
VEGF gene increased.test
methodHuman immortalized epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) were cultured with succinic extract grow (GR) cells for 24 hours, total RNA was collected, and the amount of growth factor (VEGFA) genes that promote angiogenesis was measured by RT reaction → real-time PCR method.
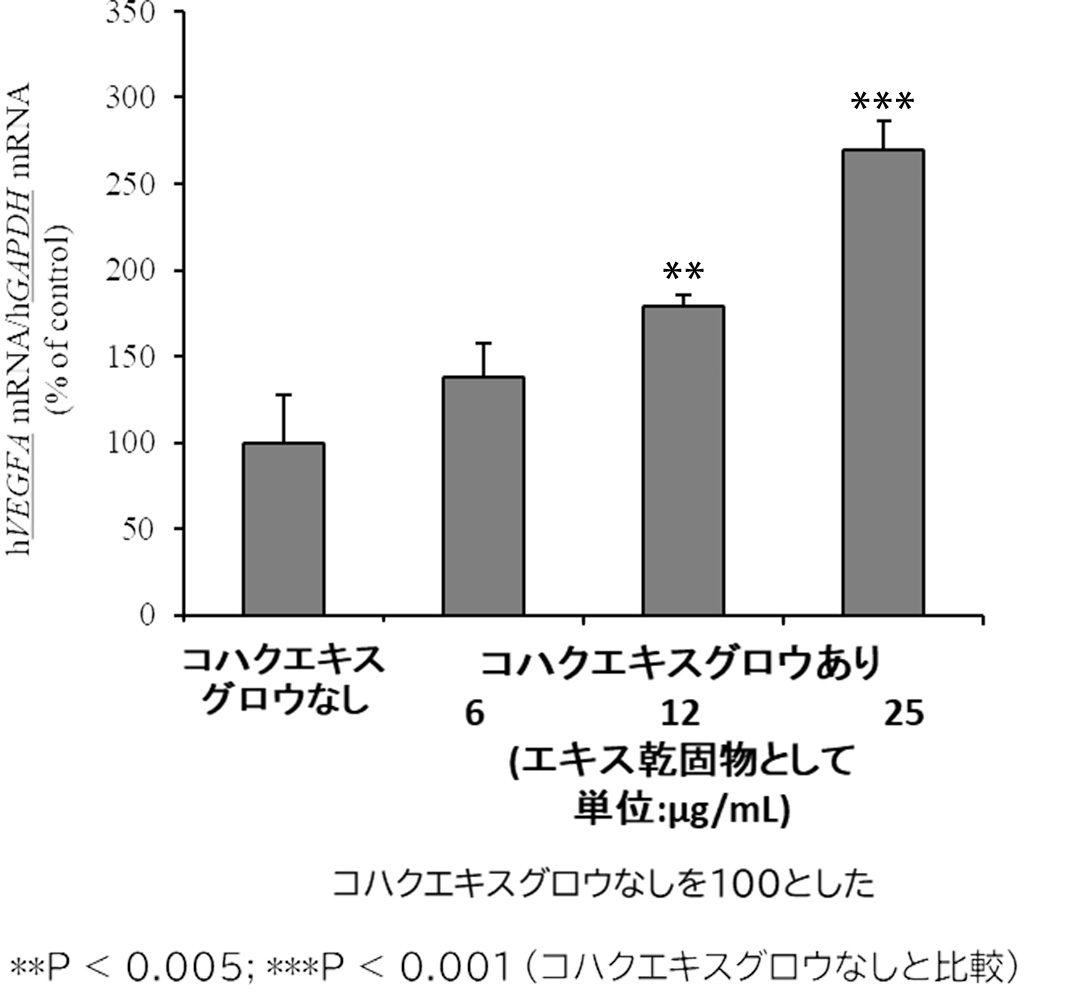 result
resultTreatment with Kohaku Extract Grow (GR) was found to increase the VEGFA gene. This is expected to increase blood circulation around hair follicles, resulting in thicker, more vibrant hair.Sato et al. (Basic research in collaboration with the National Institute of Physical and Chemical Research).
-
Chapter.3
Kohaku Extract® White (WH)
Beauty Skin EffectInhibition of melanin production (Patent No. 5858562)For KOHAKU EXTract® White (WH),
Suppresses melanin production,
It is effective in leading to blemish-free skin.Cultured human epidermal keratinocytes
Endothelin-1 genetest
methodCultured human immortalized epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT cells) were irradiated with UV light and then given succinic extract white and further cultured for 24 hours, after which total RNA was collected and gene expression of endothelin-1 was measured using the RT reaction → real-time PCR method.
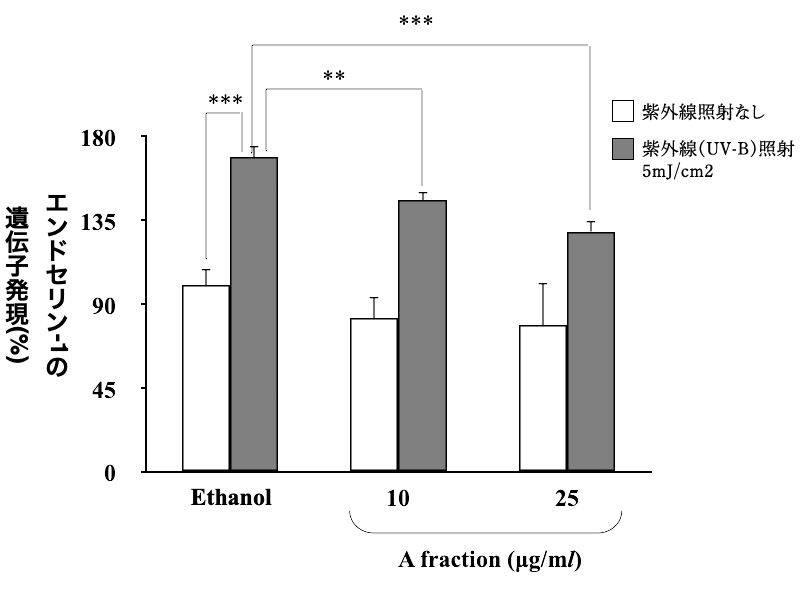 result
resultClear, blemish-free skin
It was found that gene expression of endothelin-1, an inflammatory peptide, was suppressed in those fed Kohaku Extract White compared to those that were not. This indicates that Kohaku Extract White is expected to be effective in preventing blemishes by suppressing endothelin-1, which transmits inflammation, the source of blemishes, to melanocytes.Patent No. 5656582, Drawing based on in-house data
PATENT / TREATISE
Patents / Publications
-
2023
JP 2022-10503, "Amber-containing compositions useful for prevention or improvement of periodontal pockets and their use."
-
2023
Patent Application 2022-10502, "Amber-containing compositions useful for the prevention or improvement of osteoporosis and their use."
-
2023
Behavioral and Biochemical Evaluation of Anti-Depressive and Oxidative Stress-Ameliorating Effects of Amber Extract in Adult Male ICR Mice
-
2023
Amber (Succinite) Extract Enhances Glucose Uptake through the Up-Regulation of ATP and Down-Regulation of ROS in Mouse C2C12 Cells
-
2023
Amber Extract Suppressed Mast Cell-Mediated Allergic Inflammation via the Regulation of Allergic Mediators-An In Vitro Study
-
2022
Anti-inflammatory activities of amber extract in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages
-
2022
Protective Effect of Amber Extract on Human Dopaminergic Cells against 6-Hydroxydopamine-Induced Neurotoxicity
-
2021
Amber Extract Reduces Lipid Content in Mature 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by Activating the Lipolysis Pathway
-
2021
Role of amber extract in protecting SHSY5Y cells against amyloid beta1-42-induced neurotoxicity
-
2019

Patent No. 6601860, "Glucose Absorption Inhibitor."
-
2019

Patent No. 6599592, "Alpha Glucosidase Activity Inhibitor."
-
2019

Patent No. 6548797, "Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Activity Inhibitor."
-
2019

Patent No. 6534500, "Glycerol Release Accelerator."
-
2019

Patent No. 6534500, "Glycerol Release Accelerator."
-
2015

Patent No. 5858561, "Amber-derived VEGF production stimulating agent and preparations or cosmetics containing amber-derived VEGF production stimulating agent or cosmetics for head and scalp."
-
2015

Patent No. 5858562 "Endothelin-1 production inhibitor, SCF production inhibitor, and melanin production inhibitor obtained from amber and their uses."
-
2013
Enhancement of VEGF expression and promotion of hair growth by ethanol extract of amber
-
2012

Patent No. 4953204 "Compositions containing skin turnover promoting factors obtained from amber and their use."
-
2012

Patent No. 4953203 "Compositions containing hyaluronic acid production promoting factors obtained from amber and their use."
-
2010
Effects of Amber Alcohol Extract Fraction on Promoting Skin Turnover and Hyaluronic Acid Production
-
2006
Patent No. 3741429, "Cosmetics Colored with Natural Pigments and Method for Preventing Discoloration and Fading Thereof."
-
2005
Patent No. 3741429, "Cosmetics."

